GTAW welding involves a meticulous process that demands skill and precision. Here’s a breakdown of the steps involved:
1. Preparation: Before commencing the welding process, thorough preparation is crucial. This involves cleaning the materials to be welded to remove any impurities, ensuring a clean, contaminant-free welding area.
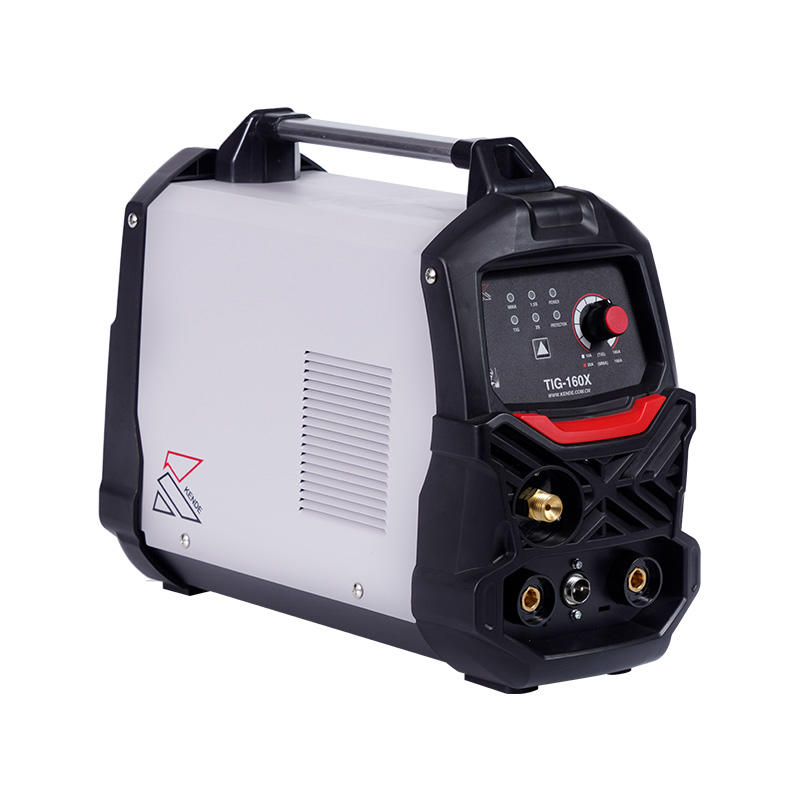
2. Setup: Once the preparation is complete, the welding equipment is set up. This includes securing the workpiece, selecting the appropriate electrode, adjusting current and gas flow rates, and positioning the tungsten electrode.
3. Arc Initiation: With the equipment set up, the arc is initiated by striking the tungsten electrode against the workpiece, creating an electric arc. Simultaneously, an inert gas (typically argon or helium) is released to shield the weld area from atmospheric contamination.
4. Welding: As the arc is established, the welder steadily guides the electrode along the joint, melting the base metals. If necessary, filler metal is added to the weld pool to reinforce the joint and ensure proper fusion.
5. Completion: Once the welding is finished, the arc is extinguished, and the weld is allowed to cool gradually, ensuring a strong and durable bond between the materials.
Advantages of GTAW Welding
Precision and Quality:
GTAW welding allows for precise control over the welding process, resulting in high-quality welds with minimal spatter.
Versatility: It can be used on a wide range of metals and alloys, including aluminum, stainless steel, copper, and more.
Cleanliness: The inert gas shielding prevents atmospheric contamination, resulting in clean, strong welds.
No Flux Required: Unlike some other welding methods, GTAW doesn't require a flux, reducing the need for post-weld cleaning.
Applications of GTAW Welding
Aerospace Industry: GTAW welding is favored in the aerospace sector due to its ability to weld thin materials without distortion and its capability to produce high-quality welds meeting stringent safety standards.
Automotive Sector: It is extensively used in the automotive industry for welding exhaust systems, chassis components, and other critical parts where precision and durability are paramount.
Pipe Welding: GTAW is commonly used in pipe welding, especially in industries such as oil and gas, due to its ability to weld various materials and produce high-quality, leak-free joints.
Challenges and Considerations
Skill Requirement: GTAW welding demands a high level of skill and precision, requiring significant training and practice.
Slower Speed: Compared to some other welding methods, GTAW welding can be slower due to its meticulous nature.
Equipment Cost: The equipment required for GTAW welding, including the power source and gas shielding, can be more expensive than for other welding techniques.

 2023.12.11
2023.12.11
 Industry News
Industry News
