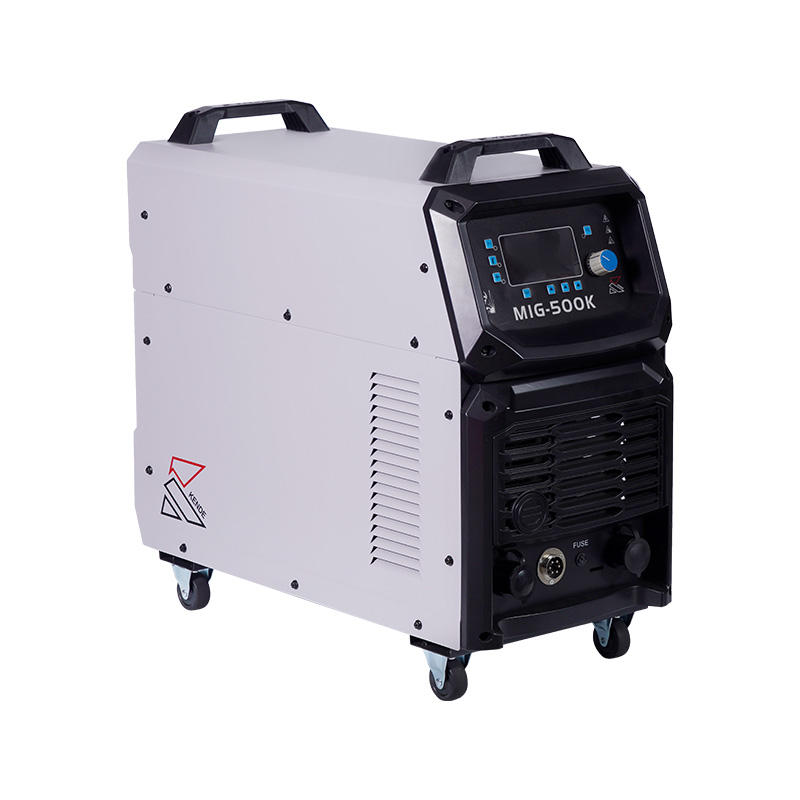
Understanding IGBT Inverters
IGBT inverters are a type of power electronic device that convert direct current (DC) into alternating current (AC). They combine the advantages of two key technologies: the high-speed switching capability of MOSFETs (Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor Field-Effect Transistors) and the low conduction losses of bipolar transistors. This amalgamation allows IGBTs to provide efficient power conversion in a wide range of applications.
Applications Across Industries
IGBT inverters are used in a plethora of industries, each benefiting from their versatile and efficient performance:
Renewable Energy: IGBT inverters are at the heart of solar and wind power systems, efficiently converting DC electricity generated by solar panels and wind turbines into AC power for the grid.
Industrial Automation: In manufacturing and automation,
IGBT inverters drive electric motors with precision and control, enhancing the efficiency of production processes.
Transportation: Electric vehicles (EVs) and hybrid electric vehicles (HEVs) rely on IGBT inverters to control the power flow from the battery to the motor, ensuring efficient and responsive propulsion.
Medical Devices: Medical imaging equipment, like magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) machines, use IGBT inverters to generate precise and controlled RF (Radio Frequency) signals for diagnostic purposes.
Renewable Energy: IGBT inverters are used in various industries for motor drives, heating, welding, and more.
High Efficiency and Energy Savings
One of the primary advantages of IGBT inverters is their efficiency. By minimizing energy losses during the conversion process, these inverters reduce electricity consumption and contribute to energy savings. This efficiency is particularly crucial in applications where power conversion is a central component of the operation, such as in HVAC systems or industrial drives.
Enhanced Control and Precision
IGBT inverters offer precise control over the output voltage and frequency, making them indispensable in applications where accuracy and reliability are paramount. This high level of control is especially beneficial in industries like robotics and semiconductor manufacturing, where precision is a must.
Integration with Digital Technologies
IGBT inverters are evolving to integrate with digital technologies, enabling real-time monitoring, diagnostics, and predictive maintenance. This digital integration allows for remote control and monitoring of systems, reducing downtime and enhancing overall efficiency.
Challenges and Advancements
Despite their numerous advantages, IGBT inverters face challenges, including heat dissipation and thermal management. Continuous research is directed toward enhancing the thermal performance of IGBT modules. Additionally, advancements in semiconductor materials and packaging technologies are improving the robustness and reliability of these inverters.

 2023.11.06
2023.11.06
 Industry News
Industry News
