Welding is the transformative process that allows us to turn raw pieces of metal into structures that shape our world. Behind every well-executed weld, there's a vast array of
welding equipment that welders rely on to bring their visions to life.
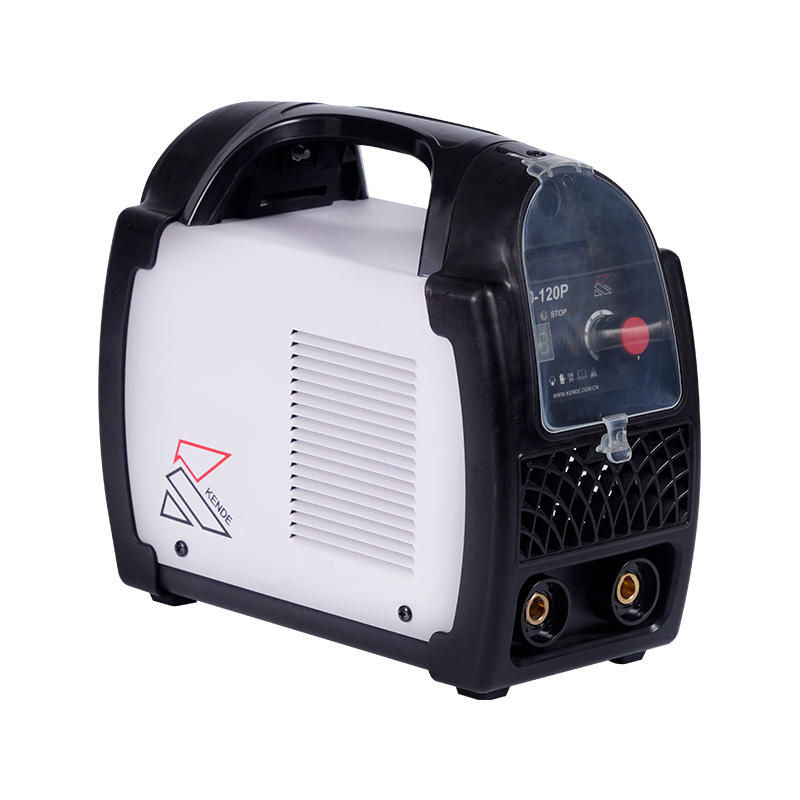
Welding Machines
At the heart of any welding setup lies the welding machine. These machines provide the necessary electrical power to generate intense heat, melting the metals being joined. There are various types of welding machines, each tailored for specific applications:
Stick Welders: Ideal for construction and fieldwork, stick welders use consumable electrodes with a flux coating to create strong welds.
MIG Welders: Commonly used in manufacturing, MIG welders employ a continuous wire electrode to create precise, high-quality welds.
TIG Welders: TIG welders offer precision and control, making them perfect for intricate work and applications where aesthetics matter.
Plasma Cutters: Beyond welding, plasma cutters are used to precisely cut through metals, making them indispensable for fabrication.
Welding Helmets and Safety Gear
Safety is paramount in welding, and welding helmets and safety gear are the first line of defense against potential hazards. Welding helmets, equipped with auto-darkening lenses, protect the welder's eyes from harmful UV and infrared radiation. In addition to helmets, welders wear flame-resistant clothing, gloves, and respirators to safeguard themselves from sparks, hot metal, and noxious fumes generated during welding.
Electrodes and Filler Materials
In various welding processes, electrodes serve as the essential link between the welding machine and the workpiece. Electrodes, coated with flux, stabilize the arc and protect the weld pool from contamination. In processes like MIG and TIG welding, filler materials are used to add material to the weld joint, enhancing its strength and integrity.
Welding Gas
In gas welding processes, such as MIG and TIG welding, shielding gases play a crucial role. These gases, including argon, helium, and carbon dioxide, protect the molten metal from the atmosphere, preventing contamination and ensuring the quality of the weld.
Welding Accessories
Welding accessories, often overlooked but highly valuable, enhance the efficiency and precision of the welding process. These include welding clamps, magnets, and ground clamps. Clamps secure the workpiece in the correct position, ensuring precise welds, while ground clamps establish a proper electrical connection, preventing electrical hazards.
Welding Power Sources
Modern welding often relies on advanced power sources to provide greater control and efficiency. Inverter-based welding machines, for instance, offer improved energy efficiency, portability, and precise control over welding parameters. These power sources are gaining popularity in both industrial and home welding applications.
Welding Automation
Automation has transformed the welding industry. Robotic welding systems are used in manufacturing to increase efficiency and consistency. Equipped with sensors and advanced programming, these systems can precisely control the welding process, resulting in high-quality welds produced at a faster pace.
Welding equipment is the backbone of modern fabrication and construction. From the welding machine that generates the heat to the safety gear that protects the welder, each piece of equipment serves a vital role in ensuring the safety and quality of welds. As technology continues to advance, welding equipment evolves, offering greater precision, efficiency, and versatility. In the hands of skilled welders, this equipment continues to shape our world, allowing us to build structures and products that stand the test of time.

 2023.10.24
2023.10.24
 Industry News
Industry News
